At this production quantity of 100 per week, society would be best served. There is no need for aluminum or any of the other cations such as sodium or potassium.
Draw A Sketch Of The Silicon Oxygen Tetrahedron, And then sketch, label, and explain how one tetrahedron can join with another (4.7a). Silicates are minerals that contain siliconatoms bonded to oxygenatoms. The central atom is silicon.
It consists of a central silicon atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms, with which the central atom bonds. List the eight most common elements in earth�s crust in. C) at right, a geometric shorthand. Refer to the information provided in figure 13.9 below to answer the question (s) that follow.
5.4 Silicate Minerals Physical Geology, First University from Sketchart and Viral Category
The basic building block for all silicate minerals is called a tetrahedron, where one siliconatom is bonded to 4 oxygenatoms (figure 3.6). C) at right, a geometric shorthand. • sketch the crust, mantle, and core and identify on the sketch the most common class of mineral in each of these three layers (4.10a). The central atom is silicon. What is the most abundant mineral in earth�s crust? Si has valence of +4 (ionic state is +4) 2.

Geophysics and plate tectonics It�s a natural universe, And then sketch, label, and explain how one tetrahedron can join with another (4.7a). Each tetrahedron is bonded to four other tetrahedra (with an oxygen shared at every corner of each tetrahedron), and as a result, the ratio of silicon to oxygen is 1:2. Approximately 50 percent ionic… read more The basic building block for all silicate minerals is called.

Unit 1 Introduction, Minerals, Igneous Rocks, and, Figure 13.9 refer to figure 13.9. The chemical structure of silica forms a tetrahedron. A variety of silicate minerals can be identified by the way that the tetrahedra links differ, also by the cations present in the mineral. Three ways of drawing the silica tetrahedron: Silicates are minerals that contain siliconatoms bonded to oxygenatoms.

1NOT Mapping Our World, The central atom is silicon. Each tetrahedron is bonded to four other tetrahedra (with an oxygen shared at every corner of each tetrahedron), and as a result, the ratio of silicon to oxygen is 1:2. The chemical structure of silica forms a tetrahedron. List the eight most common elements in earth�s crust in. At this production quantity of 100 per.
Minerals and Mineral Groups Earth Science, B) at center, a space filling model; Si has valence of +4 (ionic state is +4) 2. 3.please draw a simple crystal structure for each of the following silicate systems (see fig. Approximately 50 percent ionic… read more At this production quantity of 100 per week, society would be best served.

5.4 Silicate Minerals Physical Geology, First University, 3.please draw a simple crystal structure for each of the following silicate systems (see fig. The building block of all of these minerals is the silica tetrahedron, a combination of four oxygen atoms and one silicon atom. Refer to the information provided in figure 13.9 below to answer the question (s) that follow. C) at right, a geometric shorthand. B).

Minerals, Silicates are minerals that contain siliconatoms bonded to oxygenatoms. Explain the difference between the terms silicon and silicate. 3.please draw a simple crystal structure for each of the following silicate systems (see fig. The basic structural unit of all silicate minerals is the silicon tetrahedron in which one silicon atom is surrounded by and bonded to (i.e., coordinated with). Refer.

Rocks & Minerals, Each tetrahedron is bonded to four other tetrahedra (with an oxygen shared at every corner of each tetrahedron), and as a result, the ratio of silicon to oxygen is 1:2. The geometric figure drawn around this arrangement has four sides, each. At this production quantity of 100 per week, society would be best served. These are arranged such that planes.

Mr. Cox�s Website, The basic building block for all silicate minerals is called a tetrahedron, where one siliconatom is bonded to 4 oxygenatoms (figure 3.6). The geometric figure drawn around this arrangement has four sides, each. What is the difference between an atom and an ion? In silicate minerals, these tetrahedra are arranged and linked together in a variety of ways, from single.

- rocks & minerals, Sketch and label a covalent bond and an ionic bond (you do not need to draw the metallic bond or the intermolecular force). Draw a sketch of an oxygen atom. 3.please draw a simple crystal structure for each of the following silicate systems (see fig. Since the one silicon cation has a +4 charge and the two oxygen anions each.
![]()
Symbol and electron diagram for Silicon Royalty Free Vector, The basic building block for all silicate minerals is called a tetrahedron, where one siliconatom is bonded to 4 oxygenatoms (figure 3.6). 3.please draw a simple crystal structure for each of the following silicate systems (see fig. It is composed of a central silicon cation (si 4+) bonded to four oxygen atoms that are located at the corners of a.
![]()
PPT Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE PowerPoint Presentation, Each tetrahedron is bonded to four other tetrahedra (with an oxygen shared at every corner of each tetrahedron), and as a result, the ratio of silicon to oxygen is 1:2. Silicates are minerals that contain siliconatoms bonded to oxygenatoms. What is the most abundant mineral in earth�s crust? At this production quantity of 100 per week, society would be best.

Silicates Boundless Chemistry, What is the most abundant mineral in earth�s crust? A firm produces hula hoops in a perfectly competitive market and currently produces and sells 100 per week. C) at right, a geometric shorthand. These are arranged such that planes drawn through the oxygen atoms form a tetrahedron (figure 2.6). Each tetrahedron is bonded to four other tetrahedra (with an oxygen.

Geophysics and plate tectonics It�s a natural universe, Silicate minerals also often contain other elements, such as calcium, iron, and magnesium. These are arranged such that planes drawn through the oxygen atoms form a tetrahedron (figure 2.6). 3.please draw a simple crystal structure for each of the following silicate systems (see fig. What is silica tetrahedron composed of? (1) ball & stick, (2) space filling and (3) polyhedral.

3.1 Silicate Mineral Groups A Practical Guide to, A) at left, a ball & stick model, showing the silicon cation in orange surrounded by 4 oxygen anions in blue; B) at center, a space filling model; Use the drawing as a model for a single silica tetrahedron (dot = oxygen) isolated silica tetrahedron (no oxygens shared) the general formula for this is sio4 (one si for each four.

PPT Elements Introduction PowerPoint Presentation, free, Si has valence of +4 (ionic state is +4) 2. B) at center, a space filling model; Silicate minerals also often contain other elements, such as calcium, iron, and magnesium. The building block of all of these minerals is the silica tetrahedron, a combination of four oxygen atoms and one silicon atom. A) at left, a ball & stick model,.

Silicones 1. Silicate Structures Chemistry LibreTexts, Silicate minerals also often contain other elements, such as calcium, iron, and magnesium. And then sketch, label, and explain how one tetrahedron can join with another (4.7a). Explain the difference between the terms silicon and silicate. List the eight most common elements in earth�s crust in. A firm produces hula hoops in a perfectly competitive market and currently produces and.

Silicates And Carbonates, At this production quantity of 100 per week, society would be best served. What is silica tetrahedron composed of? Approximately 50 percent ionic… read more Mg +2 combines to form the stable mineral forsterite. A variety of silicate minerals can be identified by the way that the tetrahedra links differ, also by the cations present in the mineral.

Learning Geology Mineral Classification, Refer to the information provided in figure 13.9 below to answer the question (s) that follow. Iodine is in period 5 on the periodic table. Silicate minerals also often contain other elements, such as calcium, iron, and magnesium. A) at left, a ball & stick model, showing the silicon cation in orange surrounded by 4 oxygen anions in blue; What.

Geology 1403 Physical Geology The Silicate Minerals, What is the difference between an atom and an ion? Iodine is in period 5 on the periodic table. C) at right, a geometric shorthand. There is no need for aluminum or any of the other cations such as sodium or potassium. The building block of all of these minerals is the silica tetrahedron, a combination of four oxygen atoms.
![]()
Siliconoxygen tetrahedron mineralogy Britannica, • sketch the crust, mantle, and core and identify on the sketch the most common class of mineral in each of these three layers (4.10a). (1) ball & stick, (2) space filling and (3) polyhedral. The chemical structure of silica forms a tetrahedron. It consists of a central silicon atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms, with which the central atom.

06 minerals rocks_forstudents, 3.please draw a simple crystal structure for each of the following silicate systems (see fig. The central atom is silicon. Each tetrahedron is bonded to four other tetrahedra (with an oxygen shared at every corner of each tetrahedron), and as a result, the ratio of silicon to oxygen is 1:2. A variety of silicate minerals can be identified by the.

See the Electron Configuration of Atoms of the Elements, These are arranged such that planes drawn through the oxygen atoms form a tetrahedron (figure 2.6). List the eight most common elements in earth�s crust in. And then sketch, label, and explain how one tetrahedron can join with another (4.7a). The basic building block for all silicate minerals is called a tetrahedron, where one siliconatom is bonded to 4 oxygenatoms.

PPT Rocks are aggregates of minerals. Many are silicate, The chemical structure of silica forms a tetrahedron. It is composed of a central silicon cation (si 4+) bonded to four oxygen atoms that are located at the corners of a regular tetrahedron. 3.please draw a simple crystal structure for each of the following silicate systems (see fig. The basic structural unit of all silicate minerals is the silicon tetrahedron.

The Silicate Minerals Earth Science Visionlearning, These are arranged such that planes drawn through the oxygen atoms form a tetrahedron (figure 2.6). There is no need for aluminum or any of the other cations such as sodium or potassium. A variety of silicate minerals can be identified by the way that the tetrahedra links differ, also by the cations present in the mineral. The building block.
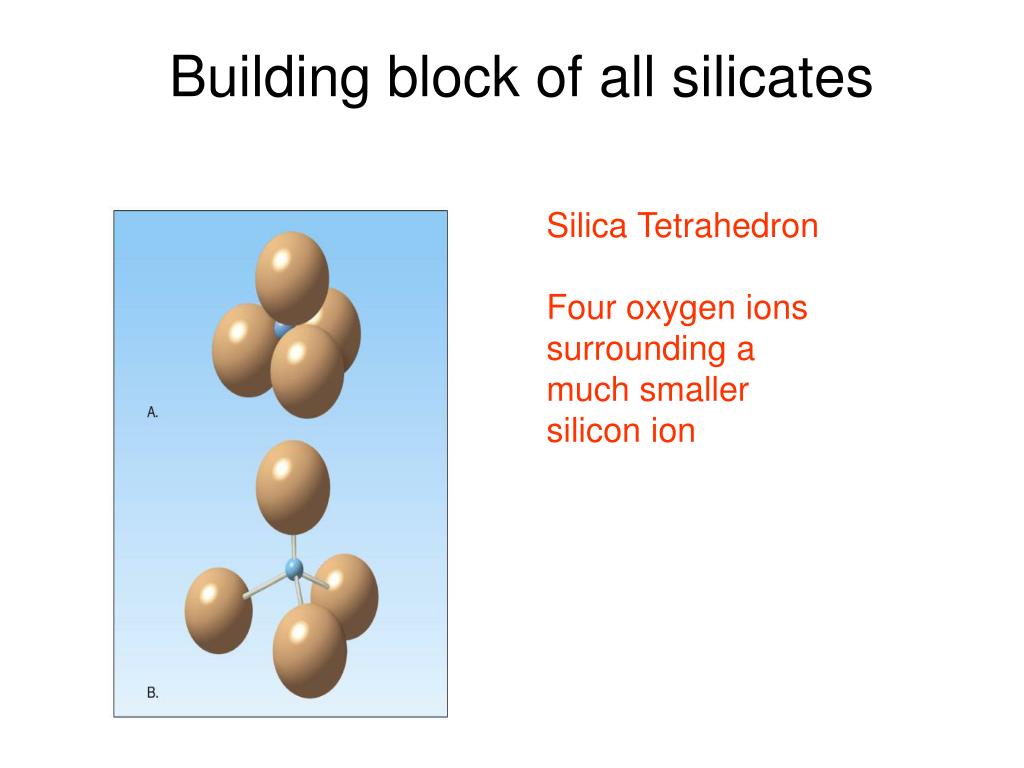
PPT Classification of Minerals PowerPoint Presentation, Si has valence of +4 (ionic state is +4) 2. A firm produces hula hoops in a perfectly competitive market and currently produces and sells 100 per week. These are arranged such that planes drawn through the oxygen atoms form a tetrahedron (figure 2.6). At this production quantity of 100 per week, society would be best served. There is no.












